5 sampling methods|types of random sampling methods : bulk Example:Researchers are conducting a study of individuals with rare diseases, but it’s difficult to find individuals who actually have the disease. . See more Legal Gambling Ages By State – States Where You Can Play Online Casinos Legally At 18+. The following is a list of all US states that allow you to gamble at 18 years old. Click .
{plog:ftitle_list}
17 de ago. de 2023 · Admito que às vezes é foda, me tiram de louco Eu ′tô na luta, eu 'tô no jogo Vou ver bike se tornar uma "hohó" Ver barraco se tornar uma mansão É, confiar no .
Example:A researcher stands in front of a library during the day and polls people that happen to walk by. Drawback: Location and time of day will affect the results. More than likely, the sample will suffer from undercoverage biassince certain people (e.g. those who work during the day) will not be represented as much . See moreExample:A radio host asks listeners to go online and take a survey on his website. Drawback: People who voluntarily respond will likely have stronger opinions (positive or negative) than the . See moreExample:Researchers are conducting a study of individuals with rare diseases, but it’s difficult to find individuals who actually have the disease. . See moreExample:Researchers want to know about the opinions that individuals in a city have about a potential new rock climbing gym being placed in the city square so they purposely seek out . See more
To draw valid conclusions from your results, you have to carefully decide how you will select a sample that is representative of the group as a whole. This is called a sampling method. There are two primary types of .Techniques for random sampling and avoiding bias. Sampling methods. Sampling methods review. Samples and surveys.
Understand sampling methods in research, from simple random sampling to stratified, systematic, and cluster sampling. Learn how these sampling techniques boost data accuracy and representation, ensuring robust, . Choose the sampling method: Select an appropriate sampling method based on the research question, characteristics of the population, and available resources. Determine .
spigen liquid screen protector drop test
Sampling strategies in research vary widely across different disciplines and research areas, and from study to study. There are two major types of sampling methods: probability and non-probability sampling.
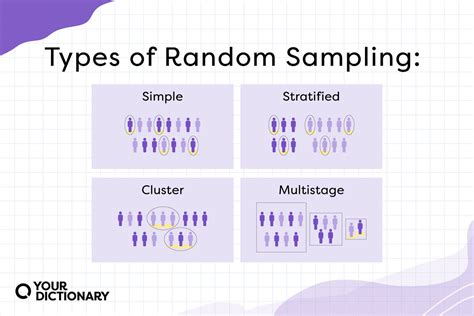
A sample is the subset of the population that you actually measure, test, or evaluate and base your results. Sampling methods are how you obtain your sample. Before beginning your study, carefully define the .The two overarching approaches. Simple random sampling. Stratified random sampling. Cluster sampling. Systematic sampling. Purposive sampling. Convenience sampling. Snowball sampling. How to choose the right sampling . When researchers want to gain insight into a large number of people, they use different sampling methods to offer a snapshot of the entire population. When properly planned, these sampling techniques can offer .
Simple random sampling. Simple random sampling involves selecting participants in a completely random fashion, where each participant has an equal chance of being selected.Basically, this sampling method is the equivalent of .
Method 5 8/2/2017 2 6.1.1 Sampling Train. A schematic of the sampling train used in this method is shown in Figure 5-1 in section 18.0. Complete construction details are given in APTD-0581 (Reference 2 in section 17.0); commercial models of this train are also available. For changes from APTD-0581A visual representation of the sampling process. In statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample (termed sample for short) of individuals from within a statistical . Sampling is one of the most important factors which determines the accuracy of a study. This article review the sampling techniques used in research including Probability sampling techniques .
For specialized insights into specific groups, non-probability sampling methods can be more suitable. 5) Get feedback. Before fully committing, discuss your chosen method with others in your field and consider a test run. Avoid or reduce sampling errors and bias. New sampling methods for slurry from the hose were substantially more reproducible than existing methods. For practical reasons, the mechanization of sampling is desirable, and to minimize the . A population is an entire group with specified characteristics. The target group/population is the desired population subgroup to be studied, and therefore want research findings to generalise to. A target group is usually too large to study in its entirety, so sampling methods are used to choose a representative sample from the target group.. A representative .
What are the sampling methods or Sampling Techniques? In Statistics, the sampling method or sampling technique is the process of studying the population by gathering information and analyzing that data. It is the basis of the data where the sample space is enormous.. There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups.
Read more: A Guide to Probability vs. Nonprobability Sampling Methods 5 types of probability sampling Here are the five types of probability sampling that researchers use: 1. Simple random sampling Simple random sampling, or SRS, occurs when each sample participant has the same probability of being chosen for the study. Consider a lottery method. Sampling methods are the processes by which you draw a sample from a population. When performing research, you’re typically interested in the results for an entire population. Unfortunately, they are almost always too large to study fully. Consequently, researchers use samples to draw conclusions about a population—the process of making .
We could choose a sampling method based on whether we want to account for sampling bias; a random sampling method is often preferred over a non-random method for this reason. Random sampling examples include: simple, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling. Non-random sampling methods are liable to bias, and common examples include . On the other hand, non-probability sampling techniques include quota sampling, self-selection sampling, convenience sampling, snowball sampling, and purposive sampling. View full-text Article
Probability Sampling Methods: Systematic Sampling. In systematic sampling, the whole sample selection is based on just a random start. The first unit is selected with the help of random numbers and the rest get selected automatically according to some pre-designed pattern. With systematic random sampling, every K’th element in the frame is selected for the sample, . Multi-stage Sampling. This method combines two or more sampling methods, such as cluster sampling and stratified sampling, to create a more complex sample design that is appropriate for the research question and the characteristics of the population being studied. How to conduct Probability Sampling
types of random sampling methods
Systematic Sampling. You can implement it using python as shown below — population = 100 step = 5 sample = [element for element in range(1, population, step)] print (sample) Multistage sampling. Under Multistage . Knowledge of sampling methods is essential to design quality research. Critical questions are provided to help researchers choose a sampling method. This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration. Probability sampling methods. Probability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that are representative .For specialised insights into specific groups, non-probability sampling methods can be more suitable. 5) Get feedback. Before fully committing, discuss your chosen method with others in your field and consider a test run. Avoid or reduce sampling errors and bias.
spigen military drop test
Non-probability sampling methods. Non-probability sampling methods don’t offer the same bias-removal benefits as probability sampling, but there are times when these types of sampling are chosen for expediency or simplicity. Here are some forms of non-probability sampling and how they work. 1. Convenience sampling
When to use simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is used to make statistical inferences about a population. It helps ensure high internal validity: randomization is the best method to reduce the impact of potential confounding variables.. In addition, with a large enough sample size, a simple random sample has high external validity: it represents the . Researchers do need to be mindful of carefully considering the strengths and limitations of each method before selecting a sampling technique. Non-probability sampling is best for exploratory research, such as at the beginning of a research project. There are five main types of non-probability sampling methods: Convenience sampling. Purposive .Types Of Sampling Methods. Here we will learn about sampling methods, including random sampling, non-random, stratified sampling, systematic sampling and capture/recapture. There are also types of sampling methods worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
random vs systematic sampling
This denoising process is called sampling because Stable Diffusion generates a new sample image in each step. The method used in sampling is called the sampler or sampling method. Sampling is just one part of the Stable Diffusion model. Read the article “How does Stable Diffusion work?” if you want to understand the whole model.
You can easily adapt the basic Method 5 sampling train to test for many other gaseous and particulate emissions from stationary sources. Adapting basic test methods allow you to expand testing to include parameters of interest such as metals, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), dioxins/furans, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), particle size distributions and an .
The selection of random type is done by probability random sampling while the non-selection type is by non-probability probability random sampling. This selection of techniques is talking about either without control (unrestricted) or with control (restricted) when individually the element of each sample is selected from a given totality, the . Q4. What are Sampling techniques in statistics? Sampling techniques in statistics are used to collect data from a sample of a population in order to make inferences about the entire population. Sampling techniques are an important part of statistical analysis, and they can be used to design a variety of different types of studies.Method 5 Determination of Particulate Matter Emissions from Stationary Sources Adopted: June 29, 1983 Amended: March 28, 1986 . A schematic of the sampling train used in this method is shown in Figure 5-1. Complete construction details are given in APTD-0581 (See EPA Method 5 Bibliography); commercial models of this train .
random vs convenience sampling
{homeTeamName} {awayTeamName} wyniki na żywo (oraz .
5 sampling methods|types of random sampling methods